Introduction
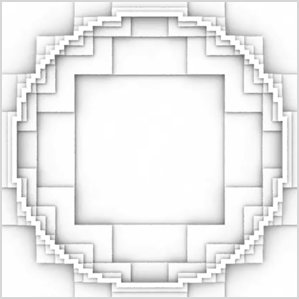
A quadtree is a data structure that stores information about a surface after it has been sub-divided into rectangles. The rectangles differ in size but the smallest are those that are considered imporatnt because they cross or contain a feature of some kind. The information about each rectangle is stored in a unit of data called a node. For example, figure 1 shows a simple subdivision in which the smallest rectangles are those that intersect the circumference of a circle.
A node stores the coordinates of the vertices a rectangle as well as a reference to the
parent node of which it is a subdivision. Some nodes also store references to
children nodes - rectangles within rectangless. There are three types of node:
ROOTnode: represents the original undivided surface,BRANCHnode: represents a subdivision,LEAFnode: represents a minimum size rectangle that interects a feature.
A root node of a has up to four children nodes but it does not have a parent node because
it represents the original surface.
Branch nodes have a parent node and may also have up to four children nodes. Leaf
nodes have a parent node but no children nodes because they represent
the minimum size subdivision.
The data in a quadtree is accumulated as a result of subdividing the original surface
in a repetitive fashion.
The process is recursive; the original surface is subdivided into four sub-rectangles
each of which is likewise subdivided. Subdivision only occurs if a rectangle spans a
feature such as a circle shown in figure 1. The process terminates when a rectangle
reaches a minimum size. The order in which rectangles are subdivided
are shown in figure 2.
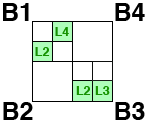
Figure 2
Quadtrees are represented as an inverted tree - the root node at the top and the leaf nodes at the bottom. An illustration of a simple quadtree is shown in figure 3. Such diagrams are called graphs.
Root
| depth: 0
------------|------------------------|
| |
B1 B3 depth: 1
|-----|---|--- |------------|
| | | |
L2 L4 L2 L3 depth: 2
Figure 3
The repetitive nature of the 1/2/3/4 recursive subdivision is clearly shown by the animation linked to figure 1.